Genomics context of missense variants
Missense variants alter the amino acid sequence that could affect the protein structure potentially leading to diseases
Missense variants leading to diseases are known as pathogenic missense variants
Missense variants with limited effects not leading to diseases are known as bening missense variants
Important
Challenges in the current clinical setting
Understanding the pathogenicity (or bening status) of missense variants is a major challenge in the current clinical setting
Over the years, scientists have identified a long list of disease associated genes.
Differentiating pathogenic and bening missense variants in these set of genes is also a challenging task
Note
Current methods to predict the pathogenicity of missense variants
Method |
Tool |
|---|---|
Evolutionary conservation |
ConSurf, FATHMM, MutationAssessor, PANTHER, PhD-SNP, SIFT, SNPs&GO |
Protein structure/function and evolutionary conservation |
Align GVGD, MAPP, MutationTaster, MutPred, PolyPhen-2 |
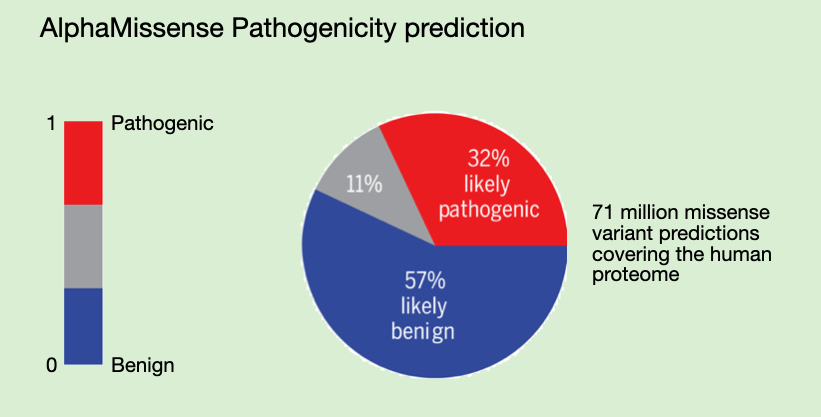
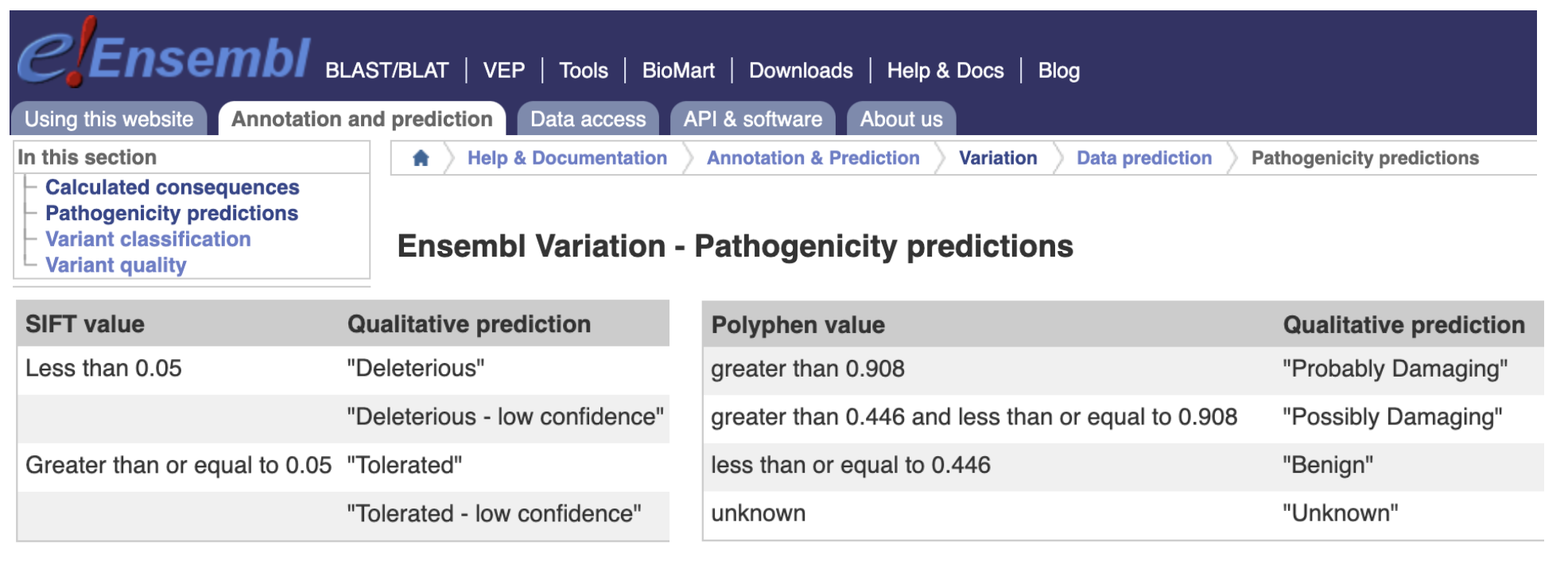
Ensembl Variation pathogenicity predictions
Ref: https://www.ensembl.org/info/genome/variation/prediction/protein_function.html
REVEL: Ensemble method that integrates scores from multiple pathogenicity predicting tools to one score
Limitations in current methods
Current tools rely on applying hard-thresholds (cut-off scores)
Practically, these hard-thresholds are used only as guides
For example, VEP user manual strongly recommends using an appropriate cut-off depending on the experiment and dataset.
These tools are used to predict the pathogenicity of other variant types (not only missense)
Tools have shown stronger pathogenicity scores for more harmful variant types (stop-gain, stop-loss, splice-site) compared to missense variants
Danger
Pathogenicity of missense variants
Predicting the pathogenicity of missense variants remains a challenging task.
A large majority of currently identified missense variants fall to the category - variants with uncertain significance
Important
Deep learning based solution