Hands-on experiment :mega:
Objective
Annotate variants in VCF file with AlphaMissense and RAVEL datasets, and then compare likely pathogenic variants identified in both methods
Main steps
Read AlphaMissense_hg38
missense proteome data(71 million missense variant predictions covering the human proteome)Read REVEL score dataset (ensemble method for combing scores from 13 tools predicting the pathogenicity of missense variants)
Reformat REVEL dataframe so that same operations can be performed for both datasets
Read variants in a VCF file and select missense variants. Then create a dataframe with variant info
Identify likely pathogenic VCF-variants based on AlphaMissense classifications
Identify likely pathogenic VCF-variants based on REVEL scores
import pandas as pd
import pysam
import seaborn as sns
Read AlphaMissense_hg38 missense proteome data (71 million missense variant predictions covering the human proteome)
am = pd.read_csv("AlphaMissense_hg38.tsv", sep="\t", skiprows=3)
am.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 71697556 entries, 0 to 71697555
Data columns (total 10 columns):
# Column Dtype
--- ------ -----
0 #CHROM object
1 POS int64
2 REF object
3 ALT object
4 genome object
5 uniprot_id object
6 transcript_id object
7 protein_variant object
8 am_pathogenicity float64
9 am_class object
dtypes: float64(1), int64(1), object(8)
memory usage: 5.3+ GB
Read REVEL score dataset (ensemble method for combing scores from 13 tools predicting the pathogenicity of missense variants)
ravel = pd.read_csv("revel_with_transcript_ids")
ravel.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 82100677 entries, 0 to 82100676
Data columns (total 9 columns):
# Column Dtype
--- ------ -----
0 chr object
1 hg19_pos int64
2 grch38_pos object
3 ref object
4 alt object
5 aaref object
6 aaalt object
7 REVEL float64
8 Ensembl_transcriptid object
dtypes: float64(1), int64(1), object(7)
memory usage: 5.5+ GB
Reformat REVEL dataframe so that same operations can be performed for both datasets
ravel = ravel.rename(
columns={"chr": "#CHROM", "grch38_pos": "POS", "ref": "REF", "alt": "ALT"}
)
ravel.drop(["hg19_pos", "aaref", "aaalt", "Ensembl_transcriptid"], axis=1)
ravel = ravel.drop(
["hg19_pos", "aaref", "aaalt", "Ensembl_transcriptid"], axis=1
).copy()
ravel["#CHROM"] = ravel["#CHROM"].apply(lambda x: "chr{}".format(x))
Read variants in a VCF file and select missense variants. Then create a dataframe with variant info
Chromosome:
#CHROMGenomic loci:
POSReference allele:
REFAlternate allele:
ALT
## Functions to read vcf file
def read_vcf_file(vcf_file):
# Open the VCF file
vcf_file = pysam.VariantFile(vcf_file)
vc_dict = {"#CHROM": [], "POS": [], "REF": [], "ALT": []}
# Iterate over each variant in the VCF file
for variant in vcf_file:
# Get the variant position and alleles
chrom = variant.chrom
position = variant.pos
alleles = variant.alleles
# Print the variant position and alleles
if (len(alleles) == 2) and (len(alleles[0]) == 1) and (len(alleles[1]) == 1):
vc_dict["#CHROM"].append(chrom)
vc_dict["POS"].append(position)
vc_dict["REF"].append(alleles[0])
vc_dict["ALT"].append(alleles[1])
return vc_dict
## Set the VCF file as a variable
vcf_file = (
"Garvan_NA12878_HG001_HiSeq_Exome_bwa-mem_CPU.sam.bam_markdup.bam_BQSR.bam.vcf"
)
## Read the VCF file and create a dataframe with missense variant info
vc_dict = read_vcf_file(vcf_file)
vc_df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(vc_dict)
vc_df.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 708845 entries, 0 to 708844
Data columns (total 4 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 #CHROM 708845 non-null object
1 POS 708845 non-null int64
2 REF 708845 non-null object
3 ALT 708845 non-null object
dtypes: int64(1), object(3)
memory usage: 21.6+ MB
vc_df.head()
#CHROM | POS | REF | ALT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | chr1 | 13684 | C | T |
1 | chr1 | 13813 | T | G |
2 | chr1 | 13838 | C | T |
3 | chr1 | 14522 | G | A |
4 | chr1 | 14542 | A | G |
## Identify likely pathogenic VCF-variants
## based on AlphaMissense classifications
am_vc = pd.merge(vc_df, am, on=["#CHROM", "POS", "REF", "ALT"])
am_vc.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 10328 entries, 0 to 10327
Data columns (total 10 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 #CHROM 10328 non-null object
1 POS 10328 non-null int64
2 REF 10328 non-null object
3 ALT 10328 non-null object
4 genome 10328 non-null object
5 uniprot_id 10328 non-null object
6 transcript_id 10328 non-null object
7 protein_variant 10328 non-null object
8 am_pathogenicity 10328 non-null float64
9 am_class 10328 non-null object
dtypes: float64(1), int64(1), object(8)
memory usage: 807.0+ KB
am_vc["am_class"].groupby(am_vc["am_class"]).size()
ambiguous 235
likely_benign 9805
likely_pathogenic 288
Name: am_class, dtype: int64
Count the number of likely_pathogenic Missense variants in the VCF based on AlphaMissense classification
len(am_vc[am_vc["am_class"]=="likely_pathogenic"])
288
Identify likely pathogenic VCF-variants based on with REVEL scores
ravel_cv = pd.merge(vc_df, ravel, on=["#CHROM", "POS", "REF", "ALT"])
ravel_cv.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 9522 entries, 0 to 9521
Data columns (total 5 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 #CHROM 9522 non-null object
1 POS 9522 non-null object
2 REF 9522 non-null object
3 ALT 9522 non-null object
4 REVEL 9522 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(1), object(4)
memory usage: 372.1+ KB
Count the number of likely_pathogenic Missense variants in the VCF based on REVEL scores
Use less stringent and more stringent thresholds recommended in REVEL publication
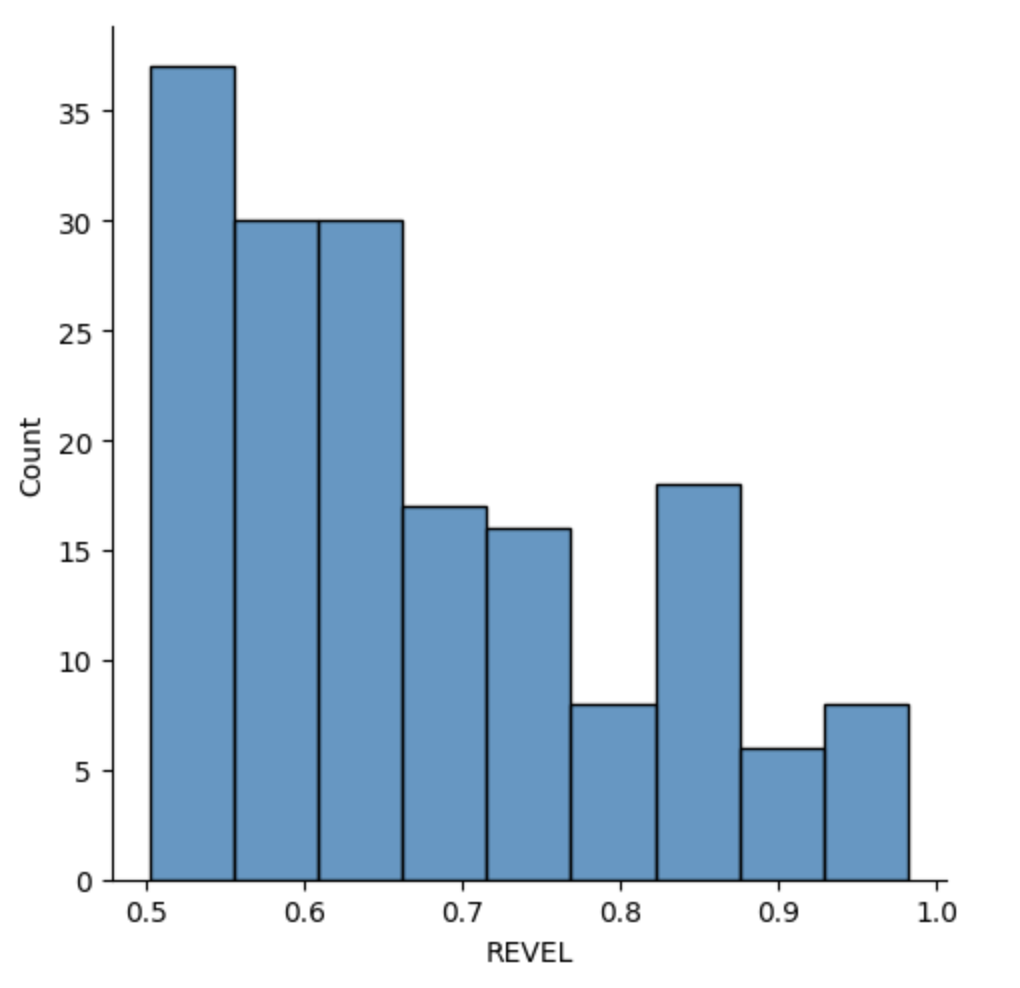
#### Count the number of `likely_pathogenic` Missense variants less stringent threshold
len(ravel_cv[ravel_cv["REVEL"]>0.5])
170
REVEL publication
REVEL score above 0.5, corresponding to a sensitivity of 0.754 and specificity of 0.891
REVEL recommends more stringent REVEL score threshold - 0.75 that lead to higher specificity but lower sensitivity, with 52.1% of disease mutations, 3.3% of neutral variants
sns.displot(ravel_cv[ravel_cv["REVEL"]>0.5]["REVEL"])
#### Count the number of `likely_pathogenic` Missense variants more stringent threshold
len(ravel_cv[ravel_cv["REVEL"]>0.75]["REVEL"])
44
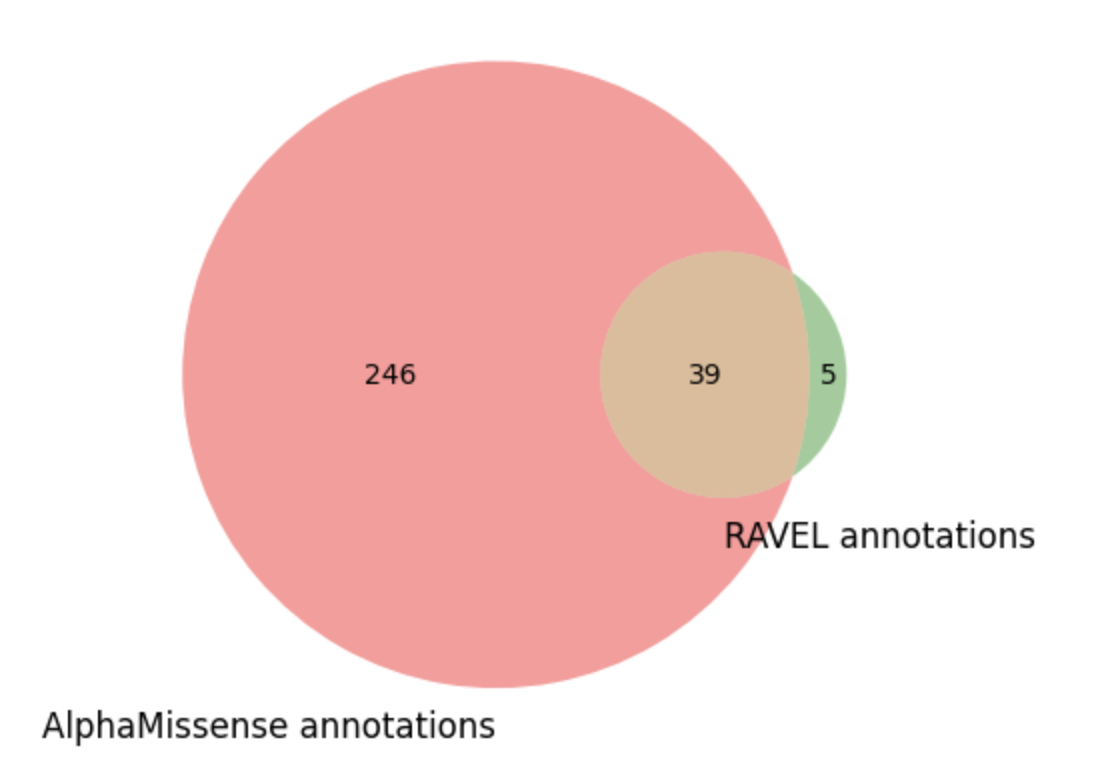
Compare VCF variant annotations - AlphaMissense classifications vs REVEL scores
### List of AlphaMissense annotated likely pathogenic variants
am_vc_list = am_vc[am_vc["am_class"]=="likely_pathogenic"].apply(lambda x: "{}_{}".format(x["#CHROM"],x["POS"]), axis=1).to_list()
len(am_vc_list)
288
### List of RAVEL score annotated likely pathogenic variants
ravel_cv_list = ravel_cv[ravel_cv["REVEL"]>0.75].apply(lambda x: "{}_{}".format(x["#CHROM"],x["POS"]), axis=1).to_list()
len(ravel_cv_list)
44
### Import plotting modules
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib_venn import venn2
Venn diagram showing the common and unique variant counts in AlphaMissense and RAVEL annotations
venn2([set(am_vc_list), set(ravel_cv_list)], set_labels = ('AlphaMissense annotations', 'RAVEL annotations'))
plt.show()